MQTT is one of the abbreviations that is often given today almost as an equation to the concept of IoT - the Internet of Things. It is not a new protocol, it appeared in 1999, for practical reasons in solving the task associated with the transmission of telemetry data. In the end, this designation still occupies half of its name. MQTT formerly: Message Queuing Telemetry Transport, today MQ Telemetry Transport. It is a simple and undemanding protocol for passing messages between clients - Publisher (sends data) and Subscriber (receives data) through a central point - Broker (takes care of data exchange). Designed by IBM, it is now backed by the Eclipse foundation and OASIS has recently been standardized. Thanks to its simplicity and simplicity, it can be easily implemented even in devices with "small" processors.
Why did we go for the MQTT protocol with Tecomat systems, which for very practical reasons focus on high performance of the central unit for processing tens and hundreds of parallel tasks in real time in the tens, maximum hundreds of milliseconds from measuring the quantity to issuing a control command or regulatory intervention? Simply because the MQTT protocol exists here. It is supported by many cloud services and the IT world demands the supply of data through this channel. And he wants more and more of them. He needs Big Data. It has prepared terabytes, petabytes, exabytes and more in data storage for them. They are happy with the technologies with which they will browse and mine the useful data from them. And hundreds or thousands of sensors can be connected to the Tecomats at once. It's time for both the IT and IoT communities to reach for Foxtrot as a multiple sensor with the ability to deliver and receive big data and respond immediately in real time.
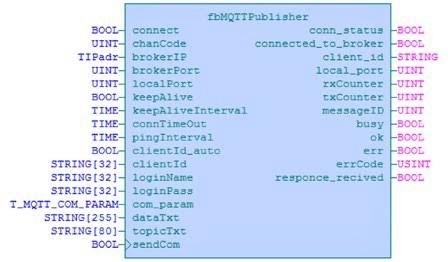
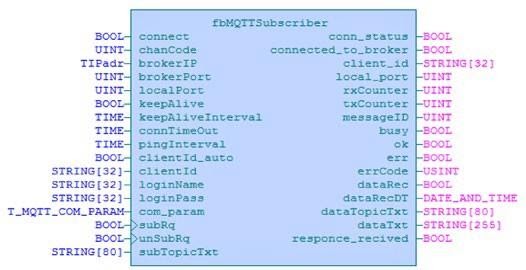
As of Mosaic v2018.1, the installation also includes the MQTTLib library. Contains the fbMQTT Subscriber and fbMQTTPublisher function blocks.
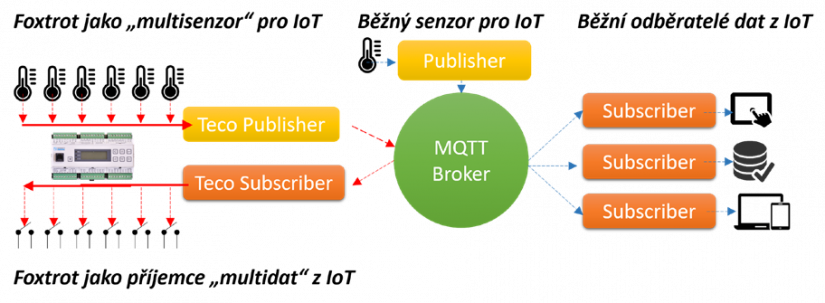
Fig. Foxtrot can play the role of a freely programmable multisensor in the Internet of Things with the function of a Publisher sending data via a Broker to Subscribers - subscribers, who can also be such a data subscriber himself and perform appropriate control functions and actions according to the data content.
